Video: “How Artificial Intelligence Will Displace Workers Worldwide”
Link: https://youtu.be/DGUeB8nSNIk
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE INTRODUCTION
Up until recently, artificial intelligence was a subject that was mostly discussed either by scientists working in the field of AI or in the movies. However, over the last few years, a surge of public, business and government interest has begun to materialize. The media has published online news articles not only on the latest AI experiments, but also a wave of reports which have examined the state of AI and its potential impacts on workers and the economic system. Businesses are acquiring startups with AI technologies and expertise, and they are purchasing and deploying AI related products as part of their digital transformation strategies. With regards to governments, some are debating how to change policy in reaction to the expected deployment of AI within the world economy, and some are making the necessary investments to help drive national innovation within the AI space.
Recently, it seems that all of that prior research and discovery made by AI researchers is creating a rapidly expanding and real world list of practical tasks that can be accomplished by AI. AI is already able to do such advanced tasks as; fly a drone, drive, translate between languages, discover new uses for existing drugs, spot cancer, analyze the genetic code of DNA to detect genomic conditions, trade stocks, do legal research, power robotics to manufacture goods, write software unit tests, and recognize emotion. Over time, scientists and engineers will be able to perfect an ever increasing database of different AI algorithms, algorithms which will be tuned to significantly outperform human analysts, consequently the usefulness and practicality of engaging humans to do work tasks will be significantly reduced.
UNITED STATES AND CHINA ARE THE DOMINANT PLAYERS
The United States has been the dominant player in AI research for decades. Up until recently, there was no true competitor anywhere in the world. However, just a few years ago, a significant surge in AI technology development has materialized at all levels within Chinese society. In just a few years time, China has caught up to the US in this key technology, and a future bipolar AI world order will unfold. Due to the nature of this technology, there are serious economic ramifications for the emerging or frontier markets. The emerging and frontier markets will not be able to leverage any future AI revenues as they do not have an AI ecosystem.
In regards to US society, Silicon Valley represents the heart of the technology industry. Corporations like Twitter and Amazon do not operate simply within the domestic market, they operate internationally. This global reach has the effect of killing innovation within local foreign markets, where foreign local start-ups do not have a chance to thrive by pulling in internet revenue to their respective markets. Though the US is often known for its military and capital markets dominance, the technical internet companies should not be overlooked as a key metric of global economic influence and power.
In regards to Chinese society, development of the AI ecosystem is being pursued by multiple actors within society. Investors are piling money into AI startups, students are enrolling in AI academic programs, the government is investing into AI initiatives and creating a supportive policy framework, and business owners are iterating through different business models and product versions. The momentum is such that it could very well be the case that China achieves its 2030 goal of becoming the global leader in artificial intelligence innovation.
AI ENTERS THE REAL WORLD

Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, has significantly advanced the field of AI. Machine learning uses algorithms to filter data, then it learns from the data, and is able to make decisions from the lessons learned. Deep learning algorithms are inspired by the human brain, and require a large amounts of data. Deep learning structures algorithms in layers to create an “artificial neural network” that can learn and make intelligent decisions on its own. Some examples of deep learning applications are: speech recognition, image recognition, natural language processing, medical image analysis, financial fraud detection, and issuing a line of credit. Deep learning will drive the profitability of technology companies for two main reasons. One, the productivity gains will be enormous. Two, many employees will no longer be required. The unfortunate aspect for society is that it is likely to lead to a widespread automation of many job roles which are currently being performed by workers across all sectors of the economy. Mass unemployment is the likely outcome.
NARROW INTELLIGENCE VS GENERAL INTELLIGENCE

To understand how AI will shape the future, we first need a light understanding of how AI works. Implementations of artificial intelligence were attempted using a “rules based” methodology and a “neural networks” based methodology. In terms of the “rules based” methodology, researchers attempted to hard code specific statements, procedures or rules so as to define a system that would follow “human style logic”. Experts were recruited to share their insight and knowledge, and this was encoded into programs with conditional statements such as “if this happens, then that will happen”. However, in terms of the “neural networks” methodology, instead of researchers attempting to teach the program rules, they focused on creating a program which could learn and which would have a similar structure to the brain. The neural networks approach involved creating a network of “artificial neurons”, a structure similar in design to biological neurons. This artificial neural structure was then fed large amounts of data, and the structure itself was able to spot correlations and patterns from the data. The more data (or examples) that is given to a neural network, the better training that the network receives, and therefore the better the program becomes at recognizing the patterns.
Deep learning involved the training of new layers, which brought about the ability to handle advanced cognitive applications. Examples of applications include “self driving cars using data from the real world” or “issuing loans using the borrowers income and credit information”. These applications are narrow functions of human ability, and are an example of “narrow intelligence”. By contrast, “general intelligence” would represent the full extent of human ability, but the AI field is very far from this capacity. Unfortunately, in the majority of cases, automated systems with narrow intelligence capability is all that is needed to replace human workers. The majority of jobs are defined in terms of their narrow and specialized functions, which could be performed by a “narrow AI” system, or a system with a few different “narrow AI” capabilities. Realizing the potential impact of AI systems on business operations, a global race to acquire top AI startups has started among the top tech companies like Google, Apple, Facebook, Amazon, and Intel.
CHINA HAS THE ADVANTAGE IN AI
China is positioned better than the United States to reap the benefits of AI. To understand this idea, we need to understand where we are in the development of this emerging technology. First, a transition from “scientific research” to “applied implementation” has taken place. The public’s idea is that we are continually making scientific breakthroughs in the field, rather than enhancing, optimizing, and generally building upon previous work. The United States would have the advantage if we would be in the “scientific research” phase of AI development, since the United States has access to elite PhD’s who know how to create and optimize mathematical and neural network algorithms. However, as we are in “applied implementation” phase of AI development, it is more important to have many entrepreneurs and engineers who can leverage scientific research and deep learning to create and deploy specialized business applications. It is the large quantity of engineers in combination with the large quantity of battle hardened entrepreneurs that gives China the competitive advantage in the “applied implementation” phase. Second, a transition from “subject matter mastery” to “data and information” has taken place. Whereas the United States may have access to a few elite artificial intelligence researchers, China has access to many more AI algorithm engineers who have access to large data sets and powerful computers. Algorithms that are created by regular engineers with access to large amounts of data will perform better than algorithms designed by elite researchers with access to smaller amounts of data. Data availability gives China the competitive advantage in the “data and information” phase.
THE COMPETITION IN CHINA

To effectively deploy AI services within an economy, four input streams are required; data, entrepreneurs, AI engineers and AI policies. By assessing these four variables, we can determine whether the United States or China will have the advantage in the future AI global economy.
China’s competitive environment can be described as extremely competitive, difficult, ruthless and mostly matter of survival. Competitor tactics are not limited to the confines of any decency or the legal system, but are open to anything that will result in a win in the marketplace. It is through practices such as; completely copying your competitors web application, stealing their domain name, using the fake domain to steal your competitors clients, calling the police on your competitor and so forth, that companies can gain tremendous success. The entrepreneurs and engineers that were forged out of this hardship, are now expert enough and experienced enough to help build the next generation of successful AI companies.
Further, China’s entrepreneurs and engineers have access to a larger amount of data than available in the United States, since China produces more data. Whereas the United States tends to capture data from the online world, China captures data from the online world and the real world as well. The combination of the two worlds, will provide China more data points and a much wider flexibility in creating AI driven solutions.
GOVERNMENT POLICIES

China has put in place a comprehensive plan to become an AI superpower. At the most basic level, this involved providing support for AI at all levels of government, and providing funding for research. In regards to research policy of the United States, though the country funds AI research in the military context, when it comes to commercial business applications, the United States has reduced funding for basic research. Also, the United States does not invest heavily into entrepreneurship. In regards to educational policy, whereas China graduates more than 600 000 undergraduate engineers annually, the United States graduates approximately 70 000 undergraduate engineers annually. The United States has not made an attempt to close this very large gap, even if could only do so by a small margin. The United States government’s lack of funding into business artificial intelligence, lack of investment into entrepreneurship and lack of educational training for the required engineers means that the United States could lose the AI race. This problem is further exacerbated when we take into account that we are both in the “applied implementation” phase and “data and information” phase, where engineer availability, entrepreneur availability and data availability is key.
The winner or winners of the AI race stand to gain global influence over non-AI enabled countries and to gain great gains in wealth from the productivity increases associated with the deployment of AI solutions. The losers of the AI revolution will have to accept a lower degree of prosperity (perhaps poverty), a lack of influence, and an inability to sell products or their values to others around the world.
AI DRIVEN INCOME INEQUALITY
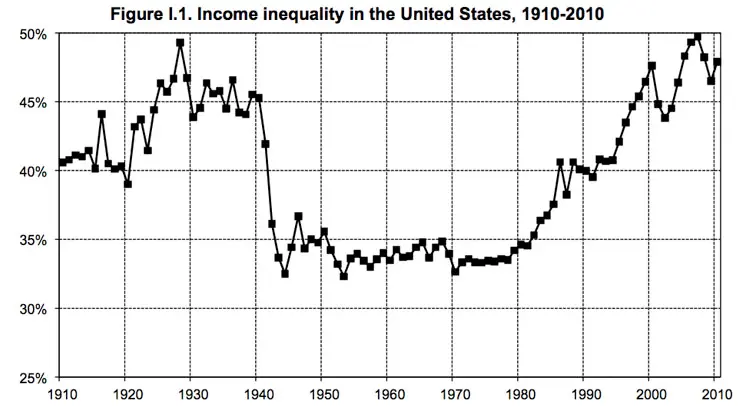
AI has the potential to further displace workers from their desired occupation than has already occurred from the other disruptive technologies already deployed. This AI disruption is likely to come at a time in history that is very precarious, as income inequality is currently at a historical high or extreme end point. Income inequality in the United States has not been at this extreme level since the stock market crash of 1929. (Y-Axis: Share of the top decile in National Income)
Workers in every industry or occupational area could be displaced. Of particular vulnerability are the white collar occupations, which so often deal with data related problems that AI excels at processing. Specifically, business, finance and technology have a great deal of vulnerability. Production jobs are at risk too. Examples of jobs which are at risk include: farmers, accountants, sales manager, security guards, radiologists, doctors, soldiers, taxi drivers, bus drivers, factory workers, receptionists, investment advisors and loan issuers.
THE AI REVOLUTION IS FASTER THAN PREVIOUS REVOLUTIONS

During the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, societies worldwide moved hundreds of millions of farmers to big industrial cities. This was a profound change, a revolutionary change. During the First Industrial Revolution, which occurred from about 1760 to about 1840, individuals transitioned to manufacturing in Europe and the United States. Almost every aspect of life changed. During the Second Industrial Revolution, which occurred from about 1870 to 1914, technological systems such as telegraph, railroad networks, gas and water supply systems, sewage systems, electrical power, telephones and more advanced manufacturing took hold. The First and Second Industrial Revolutions took about 154 years to play out. Even though there was drastic change throughout these revolutions, society was able to absorb these changes as they occurred throughout the entirety of peoples lives. The changes did not occur instantaneously, universally and exponentially throughout the entire world. AI algorithms can be deployed instantaneously throughout the entire internet, and be provided throughout the entire world for free. AI algorithms can outperform humans on quality, performance and price. A fast paced change such as this, may not be something people can adapt to overnight.
A few leading artificial intelligence researchers and a few mainstream AI publications agree on the idea that within about 15 years, technology maturity should reach the point where it will be possible to automate about 40% to 50% of jobs in the United States. However, it may take an additional decade on top of this timeline to push past the societal resistance and government policy restrictions which could stand in the way of widespread deployment and use of AI. The impact on job availability and the functional requirements of the remaining jobs will be very profound.
The integration of AI into our labour markets is expected to create both unemployment, but also to generate massive amounts of productivity, and therefore wealth for the AI owners. Domestic inequality will grow between individuals associated with AI businesses and between those unemployed as a result of AI businesses. International inequality will also grow. The two countries which have a significant AI development ecosystem in place are China and the United States, whereas the rest of the world does not have significant capabilities in AI. As such, the global economic system can end up in a situation where the two leading AI powers are able to deploy such dominant technologies, that they extract wealth from the rest of the world. AI can also challenge countries which aspire to attain developed status in a direct fashion as well. As an example, imagine the “human powered” assembly and manufacturing facilities in the developing world, are replaced with “robot powered” variants that are then moved closer to their developed world target markets. There would be no need to locate the robot factories in the poorer countries, and as such, this traditional pathway that so many countries have relied for their economic growth to developed status, would disappear. Massive global unemployment could lead to more income inequality and massive global political instability.
UPCOMING DEPLOYMENT OF AI

In the near future, deep learning will be deployed within the economy to solve real world problems. But how exactly will this take place? The availability of elite algorithm researchers within the United States technical laboratories gives the country the ability to research and optimize algorithms. What is not immediately apparent is that there are fewer scrappy entrepreneurs and engineers available for business venture creation, product implementation, and solution deployment to the market. It is this deployment step of deep learning, to automate processes within the economy, where China will excel. China has a large quantity of experienced entrepreneurs, as well as, a large quantity of engineers. Over the coming decades, these entrepreneurs and engineers will at first create domestic AI solutions, but will eventually fan out to deploy AI solutions all over the world. Businesses across the United States may not be prepared enough to deal with the heightened level of competition this scenario would present.
CHINA’S DATA ADVANTAGE

To train a good deep-learning algorithm, one needs access to: a lot of data, skilled engineers, and a lot of computer processing power. Of these three, the availability of data stands above the rest as the most important factor. Computers with large processing power are widely available, so they are not the key differentiating factor. Also, a typical engineer with access to a lot of data can optimize an algorithm to perform better than what a world class researcher can do without access to data. So the quantity of data available is the key to achieving best in class performance.
When we consider the “data environments” of China and the United States, we see that China has the data advantage. There are a lot more web users in China than in the United States, giving China a quantity advantage. Also, there exists the potential that the privacy rules within deployed software packages are not as stringent in China as they are in the United States. This would allow organizations and government institutions to collect more data on its internet users than would be possible in the United States. In addition to China’s ability to extract a large volume of information from a massive internet population, China has also set up the ability to monitor and extract information from the “real world”. This extra information should allow for the creation of not only more optimized and better performing AI solutions, but also the creation of innovative and unique AI solutions.
CHINA’S ARMY OF ENGINEERS
The widespread deployment of AI solutions to the economy will be achieved by the country with the largest quantity of motivated entrepreneurs and the largest quantity of available engineering talent, not the country with the best AI researchers. AI research publications are open and made public by the researchers, which means that the latest results are available for free to anyone who needs the information for their work. The fact that the United States has access to top notch AI researchers does not help when the real problem to be solved deals with launching technically intensive AI start ups and defeating competitors in the marketplace. At this phase in the development of the AI economy, the problem to be solved is a business and engineering problem, and not a research problem.
Further, whereas China provides generous AI contracts to business, and provides subsidizes to AI startups, the United States holds back on this kind of stimulus. There have been many wasteful financial stimulus packages created over the years in the United States, and as a result, there can be a great deal of political difficulty to get necessary funding, even for critical areas such as AI.
THE FOUR WAVES OF A.I.

Artificial Intelligence technology development and deployment is occurring in the following sequence; internet AI, business AI, perception AI, and autonomous AI. Internet AI came first, and this powers our online digital world. This was followed by business AI, and this has the ability to source information from corporate databases. Perception AI is currently being worked on, and this gives the AI the ability to “see”, perceive and interact with the real world. Autonomous AI will arrive last, and this wave will have the most impact on workers.
There are many countries which will attempt to develop and launch AI systems so as to compete with the major AI powers. It is the small country, local AI startups, where United States and China policies differ. Whereas companies within the United States seek to launch global technology solutions for everyone around the world to use, China is instead investing capital in scrappy startups across the world in an attempt to create “localized” and “unique” AI systems for domestic use.
WAVE #1: Internet A.I.
The internet companies, operating system companies, app companies, social media companies, video hosting websites and pretty much any web service which a web visitor registers to, collects personal data on client browsing history, content preferences and any other data submitted online. Using this personal data, the web services custom tailor the experience so that each visitor to their service gets served data that is most closely associated with their own personal interests and preferences. In other words, the built in internet AI recommends and serves information to visitors or clients using deep analysis from personal data.
WAVE #2: Business A.I.
Out of the four waves of AI innovation, it is business AI where the United States maintains an advantage. Corporations within the United States have years of structured data stored within their private databases, and this data can be leveraged for business purposes. Business AI can find hidden correlations within massive corporate databases, and spot patterns that a human being would never be able to find. Using the correlations, businesses will be able to make decisions that lead to better results. The United States will be able to leverage business data as part of Business AI, but China has no access to such legacy information. Instead, China will focus on engineering and adopting brand new AI systems using the best available technologies, instead of having to deal upgrading and dealing with dated digital infrastructure.
WAVE #3: Perception A.I.
Perception A.I. involves laying the “sensory framework” which can scan the physical world and convert real world data into digital data for analysis by deep learning. Perception A.I. is a prerequisite for Autonomous A.I..
WAVE #4: Autonomous A.I.
Autonomous A.I. is a result of developments from the previous A.I. stages. Autonomous A.I. combines a sensory framework with the ability to analyze data, optimize data, make decisions and interact with the real world.
THE SINGULARITY
Some people speculate that the progress in artificial intelligence is occurring at such a great speed, that society may be on the cusp of being able to create an artificial general intelligence or AGI. Artificial General Intelligence would be a computer system that is capable performing any thinking activity which a human can perform, but would be able to do so at a higher level of ability. Once achieved, the AGI could theoretically apply itself to re-designing itself, or evolving it’s own design to the point where it would achieve such a superior intelligence to humans. The AGI would become a super-intelligence that would be orders of magnitude more intelligent than human level thinking. This potential event is referred to as “the singularity”. Some optimists like Ray Kurzweil, inventor at Google, believe that we will reach the singularity by 2045. Under the optimistic scenario, humans could merge with machines, and live eternally, perhaps with their consciousness replicated within a machine environment. Others, like Elon Musk, are more pessimistic. Elon Musk equates the achievement of super-intelligence as “summoning the demon”.
TECHNOLOGICAL UNEMPLOYMENT

Income inequality is as high now as it was 91 years ago, just before the stock market crash of 1929, when the worst economic event in world history took place. Add to this the idea that the new revolutionary emerging technology of artificial intelligence is set to create widespread technological unemployment, and therefore widen the income inequality a lot further between those who have wealth and those who do not. The economic environment is set up such that any further erosion of income equality, which is likely to be brought about by the widespread adoption of AI technologies, could very well set up the world for massive political and societal instability throughout much of the world. Though artificial intelligence technologies will create massive productivity gains, and therefore profitability gains for the tech companies which employ and deploy such technologies, these gains in profit will come at the expense or loss in profit available to human labour. Even up-skilled individuals with advanced degrees and professional designations cannot and will not be able to compete with the superior performance that AI systems will bring to companies worldwide. Further, the key process that nations in the frontier and emerging markets have used to advance towards developed status, has been through manual human labour such as very low wage manufacturing jobs. When AI powered robots will be employed as part of automated manufacturing facilities, there will no longer be a route for poor nations to “manufacture” and “export” their way towards economic success. The combination of AI software and AI powered hardware in the real world will take a large toll on the vast portions of the world’s population, which are poor and have no assets that could generate income in the absence of employment related income. According to Oxfam, over half of half of humanity lives on less than $5.50 a day, and AI will have the capacity to take some of this income away.
HOW MANY JOBS CAN BE AUTOMATED?

In 2013, Oxford University researchers Michael A. Osborne and Carl Benedikt Frey, predicted that 47 percent of jobs in the United States could be automated within the span of ten or twenty years. Their study involved both surveys with machine-learning experts regarding their evaluation of the ability to automate various professions, and it contrasted that information with known “engineering limitations” in machine learning technology. Additionally, the researchers were able to create a model that showed the susceptibility levels to automation for hundreds of different professions! More recently, another team from McKinsey Global Institute came up with a similar result, when they estimated that approximately 50% of job tasks can already be automated.
THE MOST IMPORTANT POINTS

Within the developed world, certain AI enabled companies will benefit from AI technology deployment, but the young adults will not have ownership of AI assets, and as such will not have access to AI generated income. Young adults are considered a country’s greatest asset precisely because they can provide the critical productivity which a modern economy needs to function effectively and to grow. Young adults are critical for ensuring continual growth, and growth is critical for sustaining the global “debt based” financial system. Countries with young populations are often regarded by economists for their investment potential, precisely because of the wealth a young population can power an economy to generate. However, without the ability for young adults to contribute to economic growth, the young adults become yet another liability for society. Society is then faced with the stark reality that children, young adults and the elderly all end up in a dependency situation to the state. The dependency ratio then becomes unsustainable, and high levels of inflation are used to fix budget shortfalls. With government debts worldwide running at an all time and unsustainable high, governments will be unable to finance the necessary economic and physical resources which young adults will need to prosper, and even just to survive. With these circumstances in place, potentially volatile situations can erupt throughout the world. As for the developing world, these nations will not profit from AI technologies either, as they do not have ownership over any any AI enabled systems. This means that they will not have the infrastructure or AI generated income to pull their country towards economic development and growth. The poor nations will not be able to develop as a result and are likely to end up in a dependency relationship to the AI powers in the world.
UNIVERSAL BASIC INCOME OR GUARANTEED MINIMUM INCOME

Given the global economic events of 2020, Universal Basic Income (GMI) has increased in popularity and has even become a mainstream subject. Under a “Universal Basic Income” scheme, every adult of working age, whether employed or unemployed, would be given a basic income without any conditions placed on receiving it. There would be no requirements such as “job search” or “1 or 2 year time limits”. For workers, UBI would be a top-up to their existing work income. For unemployed individuals, UBI would provide the necessary income support for survival. A lesser known redistribution scheme is Guaranteed Minimum Income (GMI). GMI is a more selective application of redistribution that is means tested and available only to the poor. GMI would create an “income floor” underneath which no one could fall.
The wealth redistribution for UBI and GMI should not be fully financed by governments. Public financing of UBI and GMI would involve additional monetary printing, which would exert an inflationary force on the currency, potentially endangering government, business, and personal finances. A good source of income for UBI and GMI could be derived from the winners of the AI race. AI enabled corporations and other AI organizations will amass trillions in AI-related wealth, wealth that would otherwise go to hard working individuals. AI related wealth could be taxed for the purposes of helping to provide a UBI or a GMI. Millionaires and billionaires involved in technology automation investments could also be taxed for the purposes of helping to pay for UBI and GMI. Under the condition that AI displaces workers to such a degree that it pushes society towards protest and uprisings, then income redistribution of a small fraction of AI related income to individuals may be the only thing that stands in the way of a jobless disaster.
INVESTMENT IN “HUMAN PRODUCTIVITY” AND “HUMAN CONNECTION”

Another lesser known solution to the personal financial challenges brought about by the A.I. age, is the idea that society could invest directly in maintaining “human productivity” and “human connection”. Instead of providing a UBI or GMI where no work tasks or any responsibilities are required, society could provide an investment in “Human Productivity and Human Connection”. After all, if money is to be financed and spent publicly, why not spend it in a manner which adds to the total productivity and humanity of the nation. Opponents of this idea say that this would increase government size and add to the overall complexity of a redistribution plan. I am not convinced. How difficult could it be to have people prove via a “reference form” that they did indeed perform a task that they claimed to have performed. An income could be provided to individuals who invest their time in responsible activities that generate productivity and human connection. Examples of responsible work tasks which could be sponsored include; caregiving, learning, teaching, public infrastructure work and community support work. These five areas of work are all respected by other community members and needed for common prosperity. Individuals could be rewarded for the benefit they bring to their community, not just for the profit they can generate with their skills within a competitive globally competitive business marketplace. The investment in “human productivity” and “human connection” would not need to cover the full living expenses of an individual, but could simply be a “top up” or “inequality gap filler”, which an individual could combine with their other income and benefits. Requiring a beneficial task to be completed in order to receive a government benefit, may promote better social and economic growth. This may be better than simply receiving a payment such UBI or GMI, where no actual human productivity or human connection would be generated.
Related Content:
SGT Post on X:
@skillsgaptrainer “The rapid advancement of technology in recent decades has puzzled many, even professionals like computer scientists and engineers. Despite the time-consuming processes of research, design, development, and implementation, breakthrough technologies often seem to emerge just when they’re most needed. For instance, as markets approach potential drastic downturns, innovations like artificial intelligence technologies suddenly come into play.
The complexity of some modern technologies exceeds what is typically taught at universities, leading some to whimsically suggest that these advancements might be derived from alien technology. However, a more plausible explanation could be the extensive data collection and processing capabilities of modern operating systems and consumer electronic devices. Post-Windows XP, operating systems began to generate significant network traffic, and unusually large package of additional services, even when idle. This could indicate that operating systems and device manufacturers might be harvesting data from users. Theoretically, this data, sorted and analyzed by sophisticated algorithms, could be a gold mine for generating ideas, solving problems, and generating insights and solutions that drive technological innovations.
Given that we know there are relatively few technologists, engineers and computer scientists in North America; the phenomenon of rapid technological advancement might be less about direct employment of technologists and more about leveraging the intelligence of a global network of users who, without realizing it, may be contributing their entire life experience and professional knowledge and valuable discoveries, information, insights, expertise and original creations. This passive data collection and intelligence mining could be a key driver behind the scenes, making it unnecessary to employ traditional workers when you can analyze and utilize the data from individuals’ entire lives, personal and professional, and entire knowledge base.
The vast amount of electronic data collected via the intelligence gathering network, and the contributions users make to the internet has transformed traditional employment landscape. This wealth of data acts as a rich resource for research and development, reducing the need for hiring individuals for their data and intelligence, as companies can rely on existing data to fuel innovation and design new products and services. The combination of AI technology and the free intelligence and data from humanity, creates a unique situation where humanity does not need to be employed for non physical occupations.“
Related books and resources:
“The Fourth Industrial Revolution” by Klaus Schwab – A comprehensive look at the current technological revolution, including AI, and its effects on economies, jobs, and society. This book can give your readers a broader view of the technological changes reshaping our world.
“Humans Need Not Apply: A Guide to Wealth and Work in the Age of Artificial Intelligence” by Jerry Kaplan – Kaplan discusses the impact of AI on jobs and the economy, providing a direct link to the themes of worker displacement and economic shifts highlighted in your article.
“Life 3.0: Being Human in the Age of Artificial Intelligence” by Max Tegmark – This book explores the future of AI and its potential impacts on human life and society, complementing the more speculative parts of your post.
“The Industries of the Future” by Alec Ross – Ross looks at the industries that will shape the next twenty years, including AI. The book provides insights into how AI and other technologies will transform various sectors, aligning well with the themes of your article.
“Rise of the Robots: Technology and the Threat of a Jobless Future” by Martin Ford – This book delves into the potential economic and social consequences of widespread automation and AI, echoing concerns raised in your post about job displacement.
“The Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our World” by Pedro Domingos – Offers a deeper understanding of machine learning and its role in the advancement of AI, supporting the technical aspects of your article.
“Superintelligence: Paths, Dangers, Strategies” by Nick Bostrom – Bostrom discusses the future prospects of AI and the risks associated with it, providing a philosophical perspective that complements the more practical aspects covered in your post.
To see our Donate Page, click https://skillsgaptrainer.com/donate
To see our Instagram Channel, click https://www.instagram.com/skillsgaptrainer/
To see some of our Udemy Courses, click SGT Udemy Page
To see our YouTube Channel, click https://www.youtube.com/@skillsgaptrainer